PharmAI Now Official Maintainer of PLIP
April 22, 2020
PharmAI at BIO Digital 2020
May 26, 2020Rapid Identification of Novel PDE2 Inhibitors
Rapid Identification of Novel PDE2 Inhibitors with in silico Driven Library Prioritization and MicroScale Thermophoresis
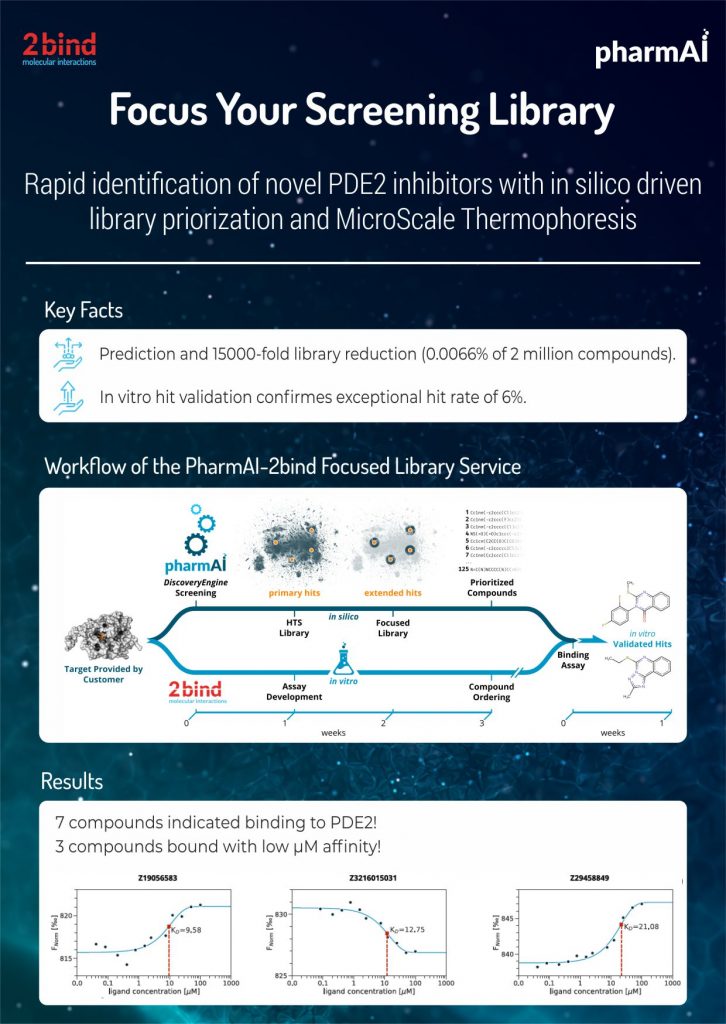
In a joint effort, PharmAI GmbH and 2bind GmbH have identified structurally novel binding compounds for the enzyme PDE2 (cGMP-dependent 3′,5′-cyclic phosphodiesterase) with unprecedented efficiency. For this, the two companies have combined an artificial intelligence-based focused-library screening approach with state-of-the-art biophysics and achieved an exceptional hit rate of 6%. With this setup, the identification of novel drugs can be accelerated tremendously.
In this project, The PharmAI DiscoveryEngine facilitated the in silico reduction of a 2-million off-the-shelf compound library to a set of just 125 structurally diverse candidate compounds. This corresponds to just 0.0066% of the whole library. The focused compound set was then screened for binding to PDE2 with a 2bind MicroScale Thermophoresis (MST) screening assay, using only 50 µg of protein and only 200 nL of each compound. Seven compounds indicated binding to PDE2, corresponding to an exceptional hit rate of 6%.
These results show how a perfect synergy between biophysics and artificial intelligence can speed up early drug discovery and deliver a process superior to standard high-throughput screenings in terms of costs and time.
Check out our latest publication for more information. (https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.22.021360v1)